Agentic AI Revolution: From Data-Driven Decisions to Fully Autonomous Enterprises
For more than a decade, organizations have invested heavily in AI – collecting data, building models, and deploying dashboards. Yet despite massive AI adoption, a fundamental gap remains:
AI still waits for humans to act.
The next wave of AI doesn’t just analyze, predict, or generate.
It plans, decides, executes, and optimizes end to end.
This is the rise of Agentic AI.
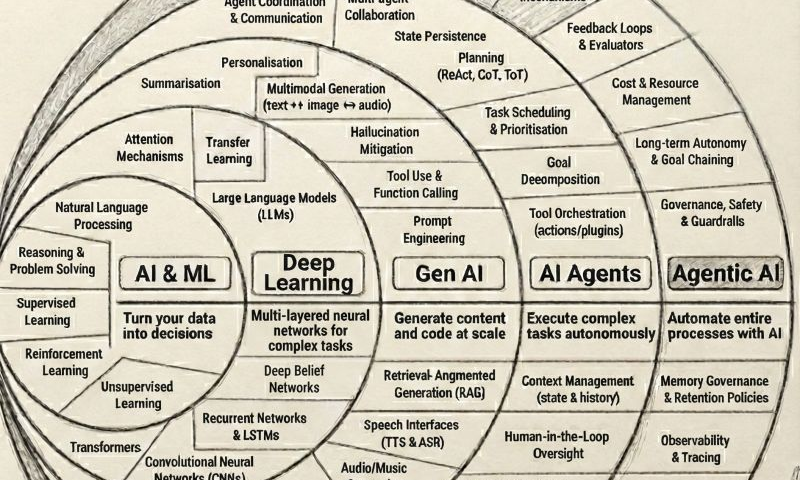
The Evolution of AI: A Clear Progression
To understand why Agentic AI is transformative, we must view it as a natural evolution, not a sudden breakthrough.
1. AI & ML: Turning Data into Decisions
This is where most enterprises began.
- Predict churn
- Forecast demand
- Optimize pricing
- Detect fraud
Outcome:
Models generate insights → humans take actions.
AI answered “What should we do?”
Humans answered “Okay, now let’s do it.”
2. Deep Learning: Handling Complexity at Scale
Deep learning pushed AI beyond rules and feature engineering.
- Image recognition
- Speech-to-text
- Recommendation engines
- Natural language understanding
Outcome:
AI handled high-dimensional, unstructured data but still stopped short of execution.
3. Generative AI: Creating Content and Code
Generative AI unlocked unprecedented productivity.
- Write content
- Generate code
- Summarize documents
- Assist with reasoning
Outcome:
AI became a co-pilot, accelerating human workflows.
GenAI says: “Here’s the content/code.”
Humans still say: “I’ll decide what to do next.”
4. AI Agents: Executing Multi-Step Tasks
AI Agents introduced goal-oriented behavior.
An AI agent can:
- Break a task into steps
- Call tools and APIs
- Observe outcomes
- Adjust actions dynamically
Example:
A marketing agent that:
- Analyzes campaign performance
- Adjusts budget
- Launches experiments
- Reports results
Outcome:
AI started acting, not just assisting but usually within narrow tasks.
5. Agentic AI: Automating Entire Processes
This is where the real shift happens.
Agentic AI is not a single agent.
It is a system of coordinated AI agents that can:
- Understand business goals
- Design execution plans
- Orchestrate multiple tools, models, and workflows
- Learn from outcomes
- Continuously optimize without human intervention
Agentic AI doesn’t ask “What should I generate?”
It asks “What outcome am I responsible for?”
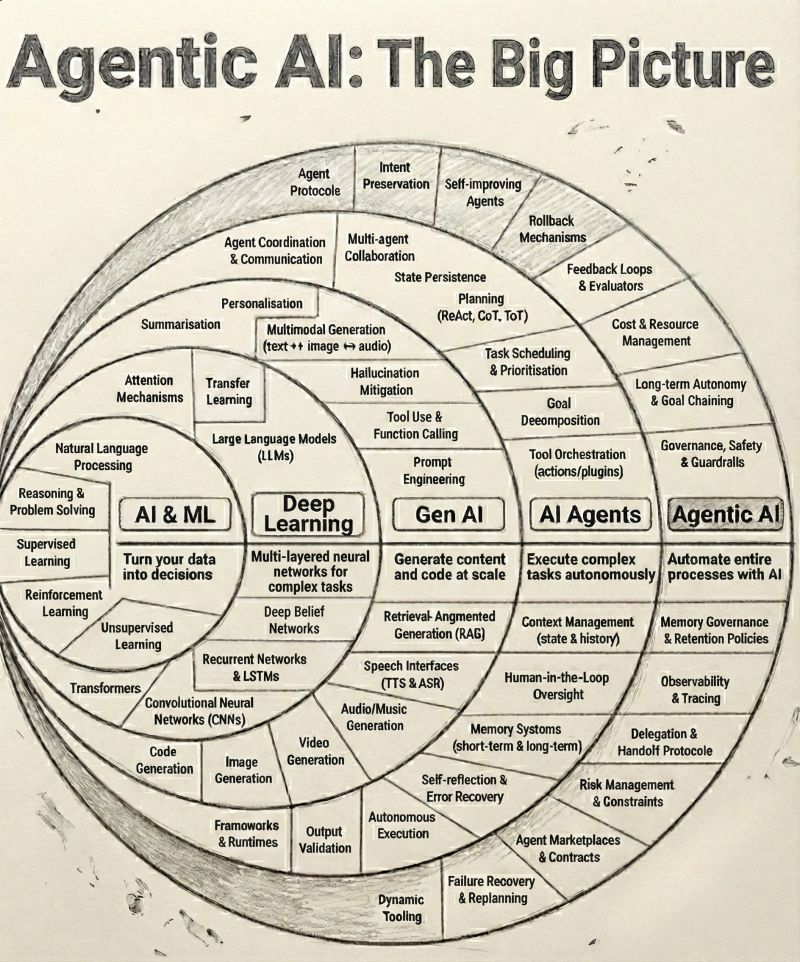
Image credit: https://www.linkedin.com/in/brijpandeyji/
What Makes Agentic AI Fundamentally Different?
| Capability | Traditional AI | GenAI | Agentic AI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insights | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Content Generation | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Tool Usage | ❌ | Limited | ✅ |
| Multi-step Planning | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Autonomous Execution | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Outcome Ownership | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
Agentic AI owns the full loop:
Goal → Plan → Act → Observe → Improve